Did you know that businesses lose an average of 20-30% of their revenue due to inefficient business processes? That's a lot of money left on the table. One of the best ways to get control of this lost revenue is through business process improvement. With the right process improvement strategy, you can identify inefficiencies and fix them, fast.
In this article, we'll share 6 simple steps to help you get started with business process improvement and maximize your ROI along the way. We’ll even provide some example process improvement strategies to inspire your own, so let’s get started.
Benefits of business process improvement
While lost revenue is certainly one compelling reason to invest time and resources into improving business processes, it isn’t the only one. With the right business process improvement strategy, you can expect to see other long term benefits including:
- Increased productivity: By streamlining tasks, eliminating wasted time, and utilizing strategies such as robotic process automation, you can increase employee productivity and increase employee engagement in high-value, strategic tasks.
- Reduced costs: By eliminating redundant or inefficient processes, business process improvement can reduce overall operational costs, resulting in increased profitability.
- Improved quality: By focusing on consistency, accuracy, and standards for quality, you can improve the overall quality of the product or service that your business is delivering to customers and prospective customers.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: Embracing continuous process improvement can lead to businesses providing more consistent, high-quality products and services to their customers, ultimating resulting in enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Competitive advantage: When your business performance is at its peak, you will inherently have an advantage over competitors who are struggling to manage everyday processes, are bottlenecked by inefficiencies, or are generally suffering to meet customer demands due to outdated processes.
6 step business process improvement guide
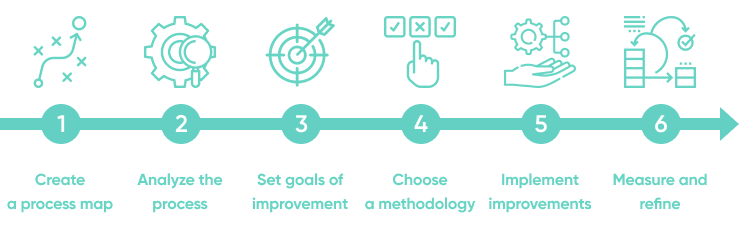
Business process improvement can be a daunting task. To ensure the best possible outcome and maximum ROI, careful analysis and strategic planning are needed to choose the right business process improvement techniques.
This 6-step guide will help you tackle business process improvement with confidence!
Create a process map
Process improvement begins by understanding the existing process: what’s working and what’s not. One of the best ways to get an understanding of an existing process is to create what’s called a process map.
A process map is a graphical representation of the steps involved in a business process, illustrating how activities and tasks are linked together. Creating a process map can bring together an entire organization and allow everyone involved to build a shared understanding of the process, which can lead to more successful improvement down the line.
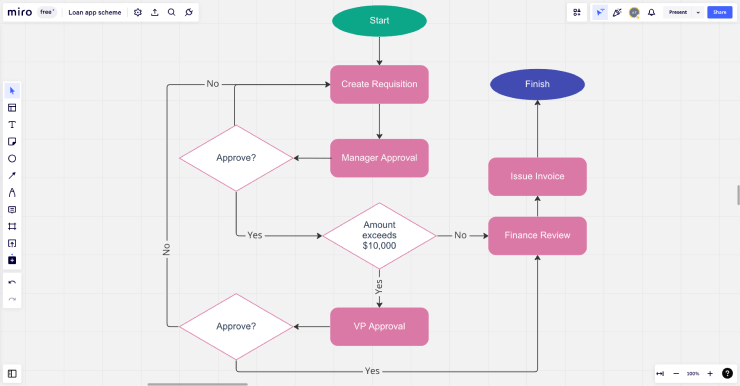
When you think of a business process map, you probably picture something like what you see below. This is called a process flowchart. It’s exactly what it sounds like: a flowchart that visualizes a process. This is one of the simplest types of business process maps and is ideal for teams who are just getting started with mapping their processes.
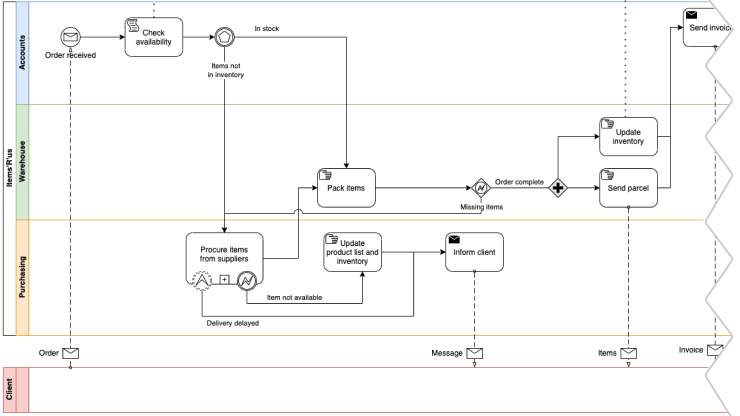
There are many other types of business process maps, some that may be more or less suited for your particular business process. For example, a business process model diagram (BPMN) like the one below is a more suitable map style for complex processes that require collaboration amongst multiple organizations or teams.
Other types of business process maps you could choose include:
- Data flow diagram
- Swimlane diagram
- Value stream map
- SIPOC flowchart
PRO TIP: Choose the right business process mapping tool. A good mapping tool should allow users to easily create and modify diagrams, collaborate with others, and track progress in real-time. Which one should you choose? It depends on what you are looking for:
- Miro is a great tool for creating collaborative business process maps. It is easy to use and provides a wide range of features such as sticky notes, boards, and whiteboards. It is ideal for teams that need to collaborate on mapping out a process and enjoy a high degree of flexibility, as it allows multiple people to work on the map at the same time.
- Lucidchart is a great option for creating business process maps quickly. It offers a drag-and-drop interface and an array of templates, making it easier to create visual diagrams. It is well suited for businesses that need to quickly create process maps or need to make changes easily.
- Draw.io is a great tool for creating complex business process maps. It offers a wide range of tools and features that allow you to create detailed diagrams. It is ideal for businesses that need to create detailed diagrams with multiple layers of complexity.
Analyze the process
Of course effective business process management requires more than simply documenting your current process. You need to analyze your process and begin to look for improvement opportunities.
This analysis should begin by reviewing your process map created in the first step, conducting interviews with those involved in the process and even reviewing software usage data, if applicable. Doing so will give you a more well-rounded perspective on the performance of each existing process. During this review, the project team should look for:
- Opportunities for process automation. Organizations should look for opportunities to automate a portion of their process. This could include using software to automate specific tasks or integrating existing systems to eliminate manual steps. Automation can increase efficiency and help businesses achieve fewer errors.
- Redundant or unnecessary steps. Look for steps in the processes that are wasting time and resources, while not providing any direct value. This can be done by analyzing the tasks and activities that are being performed and determining if they are truly necessary for the process to be successful.
- Process bottlenecks. Identify process bottlenecks by evaluating the flow of data, goods, and services and looking for places where they are being held up. Look for ways to eliminate these bottlenecks and create more streamlined, effective processes.
- Steps that require high costs. Look for points in your business processes that are costing you money. This could be points where your goods are being held in storage that you’re paying for, being transported back and forth unnecessarily, or even points where you’re paying someone to do time consuming, manual work that could be automated.
- Process dependencies: Organizations should identify any dependencies between their process and other processes and systems within the organization. This could also include identifying any upstream or downstream processes that could impact the performance of their process.
Set improvement goals
Now that you have done some initial analysis to get an idea of where the opportunities are for business process improvement, it’s time to set some specific improvement goals.
Take a look at your business KPIs at a high level. Consider how business process improvement could help you achieve your business KPIs. Do you want to improve the quality of your end deliverables? Eliminate waste? Reduce process time? Save money by adding automation or reducing inefficiencies?
Choose a few goals and align them to specific _business process KPIs _such as:
- On-time completion rate - The percentage of processes that are completed within the expected timeframe.
- Error rate - The percentage of processes that have errors or do not meet the required standards.
- Throughput - The total number of processes that have been completed in a given period of time.
- Resource utilization rate - The percentage of resources that are being used for a particular process.
- Cost savings - The amount of money saved by using a particular process.
- Customer satisfaction - The degree to which customers are satisfied with the outcome of a particular process.
- Quality - The degree to which processes are meeting the required standards and specifications.
- Profitability - A measure of the amount of profits generated by a business process relative to its cost of operation.
- Cycle time - A measure of the amount of time it takes to complete the entire process from start to finish.
Doing this will force you to be as specific as possible, which will help you achieve more success during business process improvement implementation.
PRO TIP: Create SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) to ensure that you have a clear path for achieving the desired outcome.
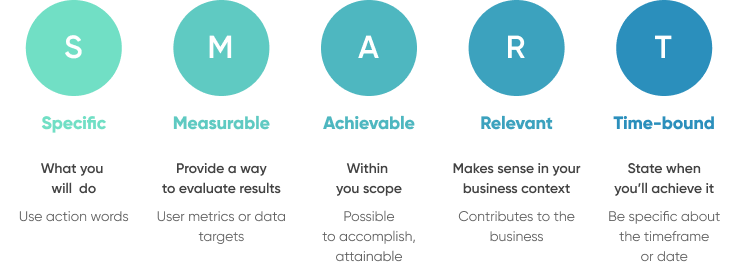
Let’s look at a few examples:
- Reduce the cycle time to launch a product by 25% within 6 months by streamlining the approval process.
- Increase the throughput of the assembly line by 10% within 6 months by implementing a more efficient process.
- Increase customer satisfaction by reducing customer wait times by 25% within two months by improving the efficiency of the customer service team.
Choose a methodology
After you’ve mapped your existing processes and set improvement goals, it’s time to decide on a methodology for implementing process changes. Doing so will help ground your improvement work and provide a framework for change implementation. There are many business process improvement methodologies to choose from including:
Lean manufacturing: Lean focuses on streamlining processes and eliminating waste; it emphasizes the importance of speed, efficiency and accuracy throughout the production process.
The key to successful implementation of Lean is to identify and analyze each step of the process and identify areas where waste can be reduced.
First, identify the current processes and use data to measure the efficiency of each step. Then, use Lean principles to identify areas where processes can be simplified or made more efficient. This may include looking for ways to:
- Reduce inventory
- Improve communication between teams
- Eliminate data errors
- Streamline transportation and production
- Reduce bottlenecks
Six sigma: Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology used to improve processes, reduce variation, and maximize efficiency. It is based on the DMAIC process, which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control:
- Define: Identify the process to be improved and define the project goal.
- Measure: Gather process data and identify areas for improvement.
- Analyze: Analyze the process data to identify root causes of defects.
- Improve: Develop and implement solutions to address the root causes.
- Control: Establish process controls to monitor and sustain process improvements.
- Total quality management (TQM): TQM is a comprehensive management approach that focuses on continuous improvement of processes and products. It emphasizes the importance of customer satisfaction and quality assurance. TQM involves all levels of the organization, from top management to the lowest level employees. TQM focuses on:
- Empowering employees and creating an environment in which they can work together to identify and solve problems
- Ensuring that employees have the tools, resources, and training necessary to do their jobs
- Establishing processes and standards to continuously monitor and improve the quality of products and services
- Encouraging customer feedback to identify areas of improvement
- Establishing a culture of accountability, where employees take ownership of their work and are held responsible for results
- Kaizen: Kaizen is a Japanese term meaning "improvement" or "change for the better". It is a business philosophy that encourages small, continuous improvements in all areas of business. In its traditional implementation, Kaizen:
- Emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement
- Relies on teams being open to change
- Focuses on improving processes through collaboration and teamwork
- Theory of constraints (TOC): TOC is a management philosophy developed by Eliyahu Goldratt that focuses on the production process and identifies the most important limiting factor (constraint) that stands in the way of achieving a goal. TOC:
- Seeks to identify and eliminate constraints in a production process.
- Is a systemic approach to problem-solving, focusing on the interaction between components of a system.
- Aims to maximize the throughput of the system by focusing on the constraint and creating “pull” in the system.
- Emphasizes collaboration and communication between stakeholders in order to identify and manage the constraint.
Implement improvements
You have set improvement goals and chosen a methodology. Now you need to implement your process changes. It’s first important to recognize some of the challenges that can come with business process improvement. First, your employees may have some resistance to changes to processes. Second, your process changes are not guaranteed to work. You may need to be flexible and adjust improvement strategies down the line.
With this in mind, draft a formal plan that outlines the objectives, timeline, and resources needed for the business process improvement project. This should include details such as who will be responsible for each task, what tools and methods will be used, what changes will be made and why, and which teams will be impacted. Here are a few tips:
- Set up a cross-functional team to lead the process improvement effort. Involving members from each impacted team can help prevent change resistance and ensure that all stakeholders’ needs are being met.
- Establish a culture of continuous improvement and develop systems for employees to identify and report process improvement ideas in the future.
- Establish standard operating procedures and training processes to ensure the successful adoption of the improved processes. Don’t neglect the need for training and staff enablement.
- Celebrate success and recognize employees’ contributions to the process improvement efforts. While it may seem unnecessary, this can go a long way.
PRO TIP: Consider the downstream effects of your process improvement work. Ask yourself questions such as:
- Will other teams be impacted?
- Do other processes need to be adjusted?
- Do documentation or training materials need to be updated?
- Has everyone involved been adequately notified of the changes?
Measure, analyze and refine
Now that you’ve implemented your changes, you need to measure and analyze the results. From there you can continue to refine your process - then repeat these three steps over time to ensure long-term success.
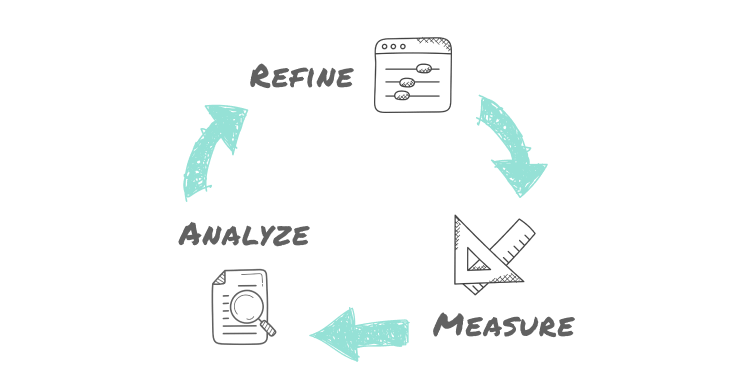
Measure: Collect data on how the new processes are functioning. This data should be collected over a sufficiently long period of time and should specifically track the process KPIs identified in step 3.
Analyze: Compare the data against the old process. What improvement are you seeing? Are there areas where you expected improvement but aren’t achieving it? Are there unexpected areas of impact? This can also be a good time to interview affected team members to get a full picture of how the new processes are working.
Refine: No process improvement strategy will have perfect results right out of the gate. Use this as an opportunity to further refine your processes.
This cycle of measuring, analyzing, refining and measuring again should be repeated until the organization is satisfied with the performance of their business process improvements.
Business process improvement examples
As we have seen, business process improvement is a critical component of any organization's success. To help inspire your next business process improvement project, in this section, we'll look at some examples of business process improvement in the areas of marketing, sales, IT and HR.
Marketing:
- Reduce the time it takes to get new banner ads approved and launched by implementing automated approval steps and reminders to approvers.
- Improve the consistency of prospect communications by implementing a CRM system that automates communications.
- Eliminate bottlenecks in the content production process by adding additional qualified content reviewers to the team.
Sales:
- Reduce inconsistent lead categorization and qualification by moving from a spreadsheet to a CRM system that has required dropdown fields with a defined methodology in place.
- Streamline the customer onboarding process by leveraging automated customer onboarding tools.
- Eliminate the need for manual contract generation by utilizing a contract generation tool.
IT:
- Reduce the time to diagnose and resolve technical issues by implementing a knowledge base and ticketing system.
- Improve team collaboration and communication by implementing a unified communication platform.
- Reduce manual maintenance tasks by automating system updates and deployments.
HR:
- Reduce time spent manually filing and retrieving employee records by implementing a cloud-based HR system that stores employee records digitally.
- Increase employee satisfaction by introducing a feedback system that allows employees to provide anonymous feedback on their working environment.
- Reduce onboarding time by introducing an automated onboarding process that provides new employees with the necessary paperwork and materials prior to their start date.
Conclusion
Business process improvement is a critical component for any organization’s success. By following the 6-step guide outlined in this article, businesses can identify inefficiencies, set improvement goals, and choose the right methodology to maximize the ROI of their business process improvement projects.
If you're looking for a business software development company to help you optimize your business processes with custom software, don’t hesitate to reach out for a consultation. With our custom business software development services you can accelerate business growth, streamline processes, and boost your bottom line.